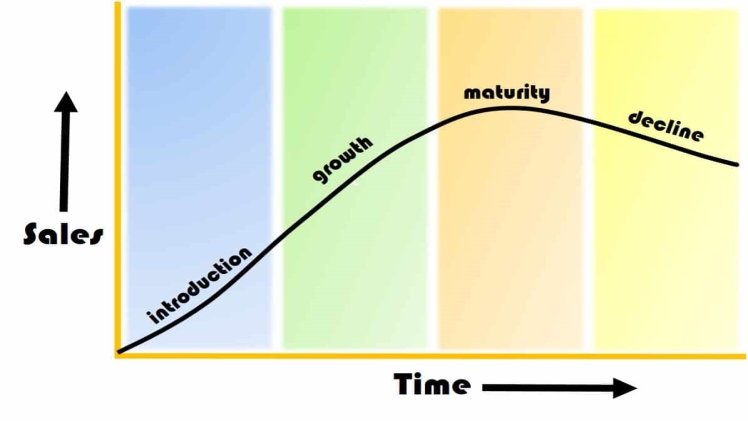
Product Life Cycle is the time during which the product goes through its various stages. It’s very similar to the human life cycle, with few exceptions. Product Life Cycle Stages are categorized based on the type of the product and its revenue stream.
Product Life Cycle Stages are:
Visit here: mediafire
- Introduction
- Growth
- Maturity
- Decline
Here are the details of each stage for further insights on what all you need to do at each stage of Product Life Cycle Stages:
Introduction Stage – The very first stage in the life cycle of a product is the introduction stage. In this phase, the sales of the product are low and promise no significant return on investments or profits made by business organizations due to lack of sales volume, etc. This phase is typically short- lived if proper marketing strategies are implemented. Here are few examples that fall under introduction stage:
- Launch of new product in market
- Trade shows/exhibitions
- Product is taught in schools
- Media advertising campaigns.
Growth Stage – The second stage of the product life cycle is the growth stage. This phase is characterized by rapid increases in sales volume, profits and market share. New product features are added based on consumer feedback to make the product more popular among masses.
Here are few examples that fall under growth stage:
- Introduction of new products with upgraded features
- Packaging innovation to attract consumers
- Increase advertising budgets for better exposure, etc.
Maturity Stage – As the name implies, maturity stage comes after initial stages of introduction and growth where a good number of consumers (ideally every customer) become aware of the product and buy it. Every customer is considered loyal to the product at this stage which results in no further growth or very little growth in sales, profits or market share. Here are few examples that fall under maturity stage:
- There might be fewer new customers getting introduced to the product, but existing consumers continue buying it
- Sales volume remains roughly stable over time
- Efficacy of advertisement campaigns declines due to saturated market
At this stage, companies start spending huge money on R & D (research & development) for the introduction of newer products with upgraded features and mostly focus on innovation rather than pure promotion (advertising costs). Declining sales figures may result in loss of customers. Here are few examples that fall under growth stage:
- Customers buying the product increase; more new customers get introduced to the product
- Sales volume increasing at a faster pace than before (accelerated growth rate)
- More money is spent on research and development for addition of further features, improvements or upgradation of existing products to attract existing or new customers.
- More money is spent on marketing and promotional activities to increase product awareness.
Companies in this stage focus on increasing market share, which requires huge investments for development of new products and services with upgraded features. This may lead towards bankruptcy if investors are not able to fund such an expansion. There needs to be a proper mix of new investments and internal cash generation for sustaining growth of the company. At times, management of these companies may get tempted and overspend on advertising or invest too much in R & D without realizing profits from their investment due to delays in the launch of new products or services, thus landing them into losses at maturity stage.
In most cases, companies move from the introduction phase through the growth stage rapidly, with a lot of new products and services being launched in a short period. This happens for two reasons: Firstly, most companies begin to generate profits from the new product during this stage due to maturity of the product life cycle. Secondly, competition also increases manifold at this stage thus creating awareness through advertisements and promotion activities which further drives sales volume. Since risk is high during this phase due to less experience in the market and lack of compatibility with customers’ needs ,it is important not to expand too fast or underestimate competitors.
In order to achieve sustainable growth throughout the maturity stage, management must focus on profitable sales driven by word-of-mouth referrals rather than heavy investments in promotions and advertisements. This can be done by either launching improved versions of existing products or by launching new products.
Decline Stage – Management must also be aware of the possibility that despite their best efforts, customer preferences may shift and affect the market share thus reducing sales volume thus leading to decline in growth rate. The decline can be stemmed by offering different variations to existing products such as price variation to target certain market segments which will still make up for a significant percentage of the company’s overall demand or by offering new products which will increase total revenue and continue to drive growth rates upwards .
Difficulties arise during this phase due to fierce competition and high demand on resources e.g manufacturing capacity and skilled labour force ,thus it is important for management at this stage to ensure that they maintain close relationships with suppliers and employees (security of jobs) as well as to ensure that they have a clear understanding of the demand schedule. In order to achieve profitable growth during this phase , management must be able to balance both short term and long term goals as sometimes it is necessary for the company to take short term losses in order to achieve better results in future profits .